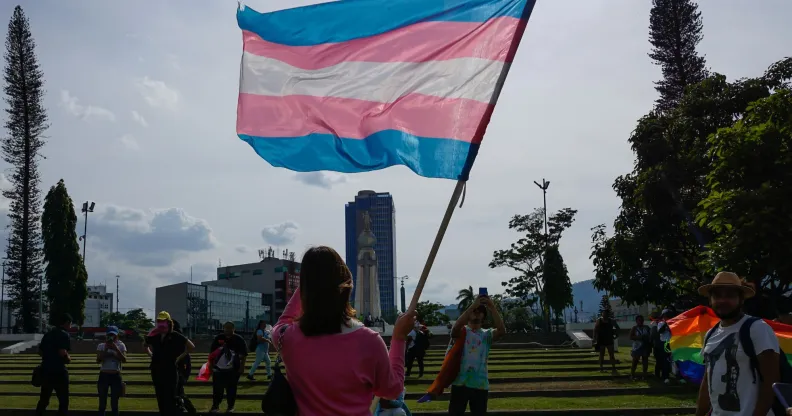
A recent study conducted by researchers at the University of College London has shed light on the challenges faced by transgender individuals living in more deprived areas. The study, published in the British Medical Journal, analyzed medical records of over seven million people, with a particular focus on the transgender community.
Deprivation and Transgender Population
The study examined the levels of deprivation in various regions, taking into account factors like employment rates, home and car ownership, income, and education. Surprisingly, cities like Nottingham and Bradford were identified as some of the most deprived areas in Britain, and it was discovered that individuals living in these areas were two-and-a-half times more likely to be transgender.
Dr. Doug McKechnie, the lead author of the study, expressed uncertainty about the reasons behind this correlation, stating, “We do not know why more individuals from deprived areas had a transgender code in their records, and if this really means that there are more transgender people in those areas, or if they are simply more likely to be recorded as such in the NHS GP records.” He pointed out that transgender individuals often face societal stigma and discrimination, which might lead to their exclusion from employment, education, and family support, potentially pushing them towards deprived areas.
Rising Numbers and Mental Health Concerns
The research also revealed a significant increase in the number of transgender individuals in the UK since the year 2000. Those reported as living with gender dysphoria rose from one in 15,000 at the start of the millennium to more than one in 2,500 by 2018. Notably, individuals aged 16 and 17 were found to be the most likely to identify as transgender.
Transgender patients also exhibited higher rates of mental health issues and substance abuse, aligning with earlier research from the Williams Institute at UCLA School of Law, which indicated that a substantial percentage of trans adults had contemplated suicide compared to their cisgender peers. Access to trans healthcare was highlighted as a crucial factor in improving the mental health and overall well-being of transgender individuals.
The findings underscore the importance of addressing the unique challenges faced by transgender individuals, particularly those living in deprived areas, and emphasize the need for better access to mental health support and transgender healthcare services.